Personal Research in 5HT2A Receptor Cascade Frequencies
In Silico Bias Profiling of LSD at the 5‑HT₂A Receptor
Background
The 5‑HT₂A receptor (PDB 6A93) is a G protein‑coupled receptor that couples to Gq/11 (activating PLC and Ca²⁺ release) and recruits β‑arrestin (leading to desensitization/internalization). LSD is known to engage both pathways with a behavioral bias toward β‑arrestin in vivo.
Objectives
- Compare Apo vs. LSD‑Bound Ensembles
- Generate ≥10 independent 10 ns replicates per condition (minimization, 150 ps NVT, 10 ns NPT).
- Sample ~5 000 frames per replicate.
- Extract Structural Markers
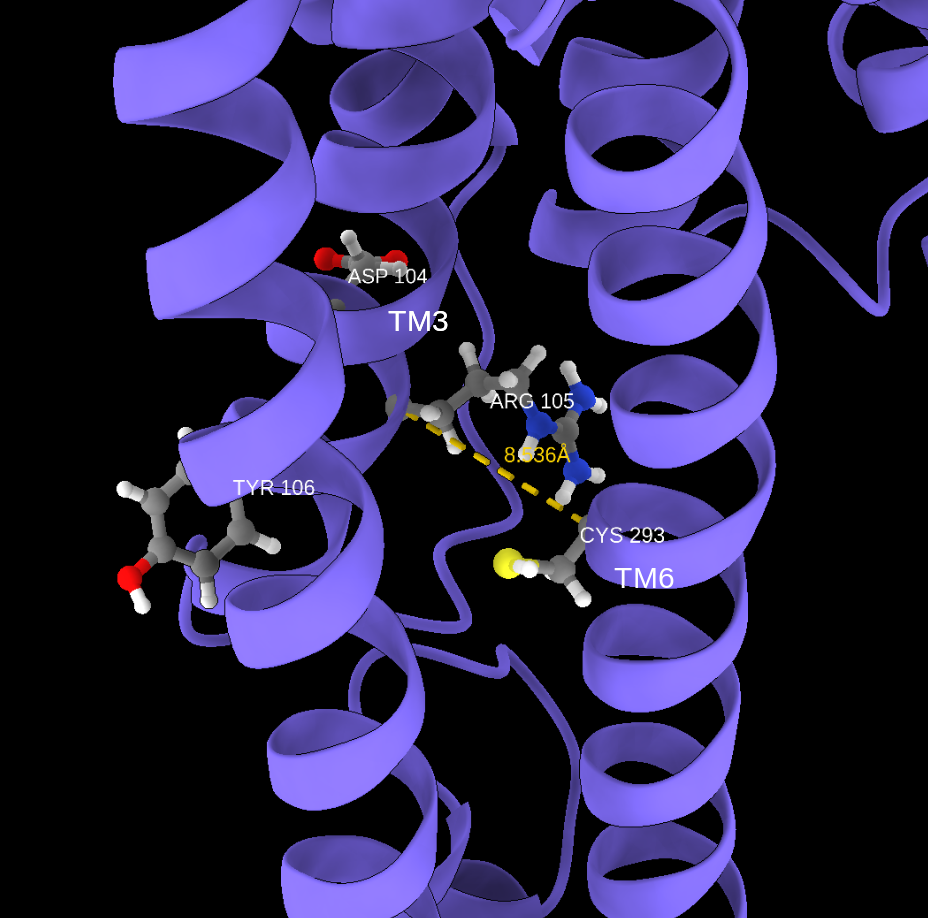
- Ionic Lock (R³·⁵⁰–E⁶·³⁰ Cα distance)
- TM6 Movement (R³·⁵⁰–L⁶·³⁴ distance)
- NPxxY Dihedral (N7.49–P7.50–x–Y7.53)
- H8 Tilt & SASA (helix 8 exposure)
- C‑tail SASA
- Principal Component Analysis & Clustering
- Build feature vectors per frame.
- Perform PCA on production trajectories.
- Cluster end‑state conformations, compare populations apo vs. bound.
- Statistical Analysis
- Per‑replicate means and 95% CIs for each metric.
- Endpoint‑state fractions (active‑like vs. inactive) with Wilson intervals.
- Group comparisons via t‑tests or nonparametric alternatives.
- Representative Arrestin‑Prone Conformation & Phosphorylation
- Identify “arrestin‑like” frames (all markers above thresholds).
- Cluster arrestin‑like pool; select centroid.
- Model key C‑tail phosphorylations (S380, T382, S384, T386) in CHARMM‑GUI.
- Run short MD to validate stabilization of arrestin signature.
Expected Outcomes
- Quantitative bias factor (Gq vs. β‑arrestin) for LSD at 5‑HT₂A.
- Structural ensemble shifts in PCA space upon LSD docking.
- In silico demonstration that phosphorylation locks in β‑arrestin–biased conformations.
Future Directions
- Long‑timescale enhanced sampling (umbrella/PLUMED) along TM6 and NPxxY CVs.
- In vitro validation via IP₃ assays and arrestin BRET.
- Extension to other psychedelics and receptor subtypes.
Photos